
All Sexual Health Topics
Upcoming Events

- Sexual Health Topics: Men’s Sexual Health, Women’s Sexual Health
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic disease that can cause joint inflammation all over the body, particularly in the hands, knees, and feet. RA is also an autoimmune disease, which means the body’s immune system attacks its own healthy cells.

- Sexual Health Topics: Men’s Sexual Health, Women’s Sexual Health
High blood pressure (also called hypertension) can damage blood vessels in your body, including the genitals. It’s also linked to atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries), which can cause your blood vessels to narrow and make it harder for blood to flow through.

- Sexual Health Topics: Men’s Sexual Health, Women’s Sexual Health
Hemophilia, a bleeding disorder, occurs when the body has lower-than-normal levels of certain proteins that help clot blood. (These proteins are called clotting factors.) As a result, bleeding can be difficult to stop. Sometimes, it happens spontaneously.
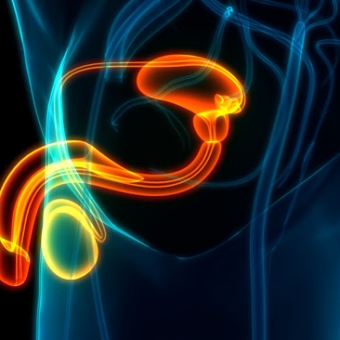
- Sexual Health Topics: Men’s Sexual Health, Cancer & Sexual Health (Oncosexology), Sexual Health Management & Treatments, Sexual Orientation & LGBTQIA+ Health
Located in the scrotum, the testicles (also called the testes) are a pair of glands that produce sperm cells and testosterone, the primary sex hormone and anabolic steroid in males. Testosterone plays a key role in the development of male characteristics. It is involved with sex drive, erections, and sperm production. It also helps build muscle and bone mass.

- Sexual Health Topics: Men’s Sexual Health, Women’s Sexual Health
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a condition that affects the large intestine and digestion. Symptoms vary from person to person, but they can include pain, abdominal cramping, bloating, constipation, and diarrhea. IBS can be unpredictable. You may not know when symptoms will start.








